We’re living in an era of digital transformation, where technology is rapidly advancing, and businesses are seeking innovative ways to enhance productivity, efficiency, and scalability. One of the latest buzzwords in the tech industry is Hyperautomation.
Hyperautomation is considered to be the future of automation and is expected to revolutionize the way we work. However, some people are still unaware of this new concept and are wondering what it means and how it can benefit their businesses.
In this article, we will explain the concept of Hyperautomation and its Benefits.
Introducing Hyperautomation and How it is Different from Traditional Automation
Hyperautomation goes beyond traditional automation by integrating advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) with process automation. While traditional automation is confined to executing predefined tasks, Hyperautomation is about designing and automating end-to-end business processes.
This not only fosters increased operational efficiency but also brings about an improvement in decision-making, thanks to the incorporation of AI and ML for data analysis and decision support.
In other words, Hyperautomation takes automation to the next level, enabling an intelligent, interconnected, and autonomously operating business environment.
Explaining the Core Components of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is built upon a combination of several key components, each contributing to its overall functionality.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): This technology enables the automation of routine tasks through software bots. RPA is particularly effective for tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and involve structured data.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI offers capabilities such as natural language processing, speech recognition, and decision-making. It allows systems to learn, reason, and self-correct, enhancing the intelligence of automation.
Machine Learning (ML): In the context of Hyperautomation, ML aids in understanding patterns and making data-driven decisions.
Process Mining Tools: These tools provide insights into business processes, helping to identify areas that can benefit from automation. Process mining tools analyze data logs to discover, monitor, and improve upon existing business processes.
Advanced Analytics: These analytics tools help businesses understand the effectiveness of their hyperautomation efforts and identify areas for improvement.
Benefits of Hyperautomation
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Hyperautomation eliminates repetitive, manual tasks by automating them, leading to increased efficiency and reduced errors.
Cost Savings: By automating processes, organizations can significantly reduce labor costs and operational expenses associated with manual tasks.
Faster Decision-Making: Hyperautomation provides real-time data and insights, enabling businesses to make more informed and timely decisions.
Improved Customer Experience: With hyperautomation, organizations can provide faster response times and personalized experiences to customers.
Agility and Adaptability: Hyperautomation equips organizations with the flexibility to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and business requirements.
Cross-Functional Integration: Automation tools can integrate disparate systems and processes, breaking down silos and promoting seamless information flow across different departments or functions.
Risk Mitigation: Automation can minimize risks associated with human error, security breaches, and compliance violations by enforcing standardized processes and security protocols.
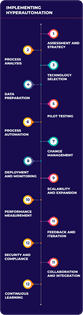
How to Implement Hyperautomation in Your Business
Assessment and Strategy:
- Identify processes for automation.
- Define objectives and priorities.
Process Analysis:
- Map workflows and tasks.
- Find automation opportunities.
Technology Selection:
- Choose fitting automation tools.
- Consider integration capabilities.
Data Preparation:
- Clean and secure data.
- Ensure compliance.
Pilot Testing:
- Test automation in a controlled setting.
- Address issues and improvements.
Process Automation:
- Build automated workflows.
- Integrate with systems.
Change Management:
- Communicate benefits to employees.
- Provide necessary training.
Deployment and Monitoring:
- Implement in production.
- Continuously monitor performance.
Scalability and Expansion:
- Expand automation gradually.
- Adapt to evolving needs.
Performance Measurement:
- Set KPIs for evaluation.
- Regularly analyze results.
Feedback and Iteration:
- Gather and act on feedback.
- Make iterative improvements.
Security and Compliance:
- Maintain robust security measures.
- Ensure regulatory compliance.
Collaboration and Integration:
- Foster cross-departmental teamwork.
- Optimize end-to-end processes.
Continuous Learning:
Potential Pitfalls of Utilizing Hyperautomation
Lack of skilled personnel: Implementing hyperautomation requires a workforce skilled in AI and Machine Learning. A shortage of such skills can impede the successful implementation and management of these advanced tools.
High initial costs: The introduction of hyperautomation could entail high initial investment costs, potentially deterring smaller businesses.
Resistance to change: Employees may resist the shift to hyperautomation due to fear of job loss or the perceived complexity of new tools and processes.
Data privacy: With the increase in data processing, organizations must pay careful attention to maintaining data privacy and meeting regulatory compliance guidelines.
Overreliance on automation: While automation can streamline operations, an overreliance on it can be problematic. Human oversight is still necessary to manage unexpected situations and make complex, strategic decisions.
In conclusion, successful hyperautomation implementation requires careful planning, skilled manpower, sufficient funding, and a robust change management strategy.
Conclusion
Hyperautomation, with its ability to streamline operations and promote efficiency, is a pivotal trend that businesses need to embrace in this digital age. Despite potential challenges such as high initial costs, resistance to change, and data privacy concerns, the benefits undoubtedly outweigh these obstacles.
As long as organizations are equipped with a strategic roadmap, the right set of tools, and a skilled workforce, they can leverage hyperautomation to drive growth, agility, and competitive advantage.