If you don’t invest in risk management, it doesn’t matter what business you’re in, it’s a risky business – Gary Cohn
The act of software development is not the outcome of a few unplanned, spontaneous actions. The Software Development Life Cycle is an elaborate and detailed procedure, of which the phase of Software Testing is crucial.
It helps determine a specific software product’s quality requirements and standards. Now imagine a situation where you have expended a considerable amount of resources, time, and effort in order to push a product towards its launch, only to find a single defect in the production, which can ruin all your toil and labor.
So, how do you save yourself?
The answer lies in practicing Risk Management in Software Testing. But what is Risk Management in Testing? Let us try to explore.
In this blog, we shall explore the concept of Risk and Risk Management in Testing. We shall also look at the Risk Management Examples in Software Testing, the different and varied kinds of risks which might emerge as well as the Risk Management Process in Software Testing.
What is Risk and Risk Management in Software Testing?
Risk can be understood as the probability/possibility of the occurrence of an unwanted/undesirable event or an encounter with an adverse result. The process of Risk Analysis entails the identification of risks associated with the Testing project.
Failure to mitigate risks can result in dissatisfied customers, negative cost impact, adversarial user experience as well as loss of clients. Hence, organizations seek to conduct Risk Based Testing.
Risk Based Testing can be understood as an approach to conducting relevant testing to identify business risks that can potentially pose significant damage to the organization’s stature. The objective of RBT is to detect risks early on in the life cycle of a software product and, accordingly, develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
The RBT approach uses the basis of prioritization for determining the degree of risk associated with different modules, features, or functionalities of a product and accordingly decide upon which aspects of the end product need to be tested and addressed.
So what is Risk Management in Testing? Risk Management in Software Testing refers to the process of detecting, evaluating, and prioritizing risks in order to diminish, regulate, and control the possibility of undesirable outcomes.
Hence, the Risk Management Process in Software Testing basically prepares us to comprehend, prevent, identify, and overcome risks.
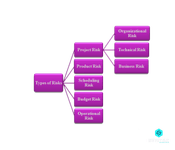
Different Categories of Risks
In this section, we will examine some of the prominent risks associated with a software project.
1. Project Risk
This category includes all those risks that have the potential to stall or negatively affect the progress of a project.
- Organizational Risk
This category includes risks that are primarily associated with your testing team or the human resources of your organization. It might be in the form of scarcity of manpower, lack of skilled personnel and so on.
- Technical Risk
It includes the possibility of loss that might be incurred as a result of the execution of a technical process.
- Business Risk
This is generally a risk emanating from an external party and not from the project under consideration. It might come from the customers or be the result of any untoward incident that the Company faces. For instance, financial loss for the Company might push the top management to slash the project budget, which will only result in aggravating problems for those responsible for executing the project.
2. Product Risk
This category includes all risks that might result in a software product’s failure to meet the expectations and needs of stakeholders, customers, or users. It is essentially associated with a product’s functionality and might take the form of Security Concerns, Performance Issues, Crash Reports, and so on.
In addition to these major categories of risks, there are certain other variants of risks as well. Such as:
- Scheduling Risks: These arise when projects are not completely or efficiently scheduled for meeting the deployment deadline.
- Budget Risk: It arises when the top management ends up inaccurately estimating the required investment.
- Operational Risk: It includes system failures, ineffective processing or unforeseen circumstances.
Why provide for Risk Management in Testing?
Failure to manage risks efficiently can prove to be fatal for the interests of the organization concerned. Risk analysis not only helps in identifying and detecting risks, but also in developing appropriate measures for managing and mitigating them. In this section, we shall look at some of the reasons why Risk Management in Software Testing is extremely important. Failure to mitigate risks can result in:
- Reduced ROI
- Compromised Quality of the Software Product
- Overstretching the Deployment Deadline
- Failure to meet Project Obligations
- Increase in Production Cost
- Customer Dissatisfaction
Given the disadvantages that might accrue from failing to provide risk management, it becomes imperative to make room for it. Risk-based testing or Risk Analysis is an important component of this. It helps in providing testing to ensure customer satisfaction from a business perspective. It helps in optimizing QA efforts and meeting the time schedule with expected quality.
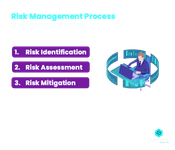
Risk Management Process in Software Testing
The question of whether or not you should provide for Risk Management in Testing is settled. The answer is definitely yes. So once you have decided to conduct Risk Management, what steps should you follow to guarantee it? Let us look at the Risk Management Process in Software Testing.
Risk Identification/Detection
In the first phase, you are obliged to sift out every possible cause or issue which you think might adversely affect the future course of events. The objective here is to chalk out a list of risks. The act of Risk Identification is collectively performed by the entire QA team. It is important to remember that this kind of detection is supposedly conducted in the planning phase itself, and thus, the risks identified here are more managerial in nature and do not really focus on the functionality of the Application Under Test. Some of the common risks enumerated in this stage include:
- Shortage of Resources
- Tight Test Schedule
- Incomplete definition of Scope
- Delayed Testing
- Natural Disasters
- Unclear Specifications resulting in Defects at a later stage
- Non-availability of independent Test Environment
In the process of identifying risks, usually one or the other methods are followed.
- Conducting Independent Reviews
- Retrospective Meetings
- Acquiring Opinion from Experts
- Brainstorming, along with Conducting Risk Workshops
- Existing Templates of Risks
- Revisiting Previous Experience
Risk Assessment/Risk Impact Analysis
In the Risk Management Process in Software Testing, the step of Risk Assessment is believed to be quite a complex one and should be handled with utmost care. The assessment phase needs to be dealt with programmatically as it entails the need to assign a level of risk to each of the item identified in the first phase. This step involves the quantification and prioritization of all the risks. Effort is directed towards identifying the probability (possibility of occurrence) and impact (the kind of loss that might result from the risk) of the detected risks.
Low-medium-high values are assigned to the probability and impact of each risk. Accordingly, those risks that end up getting high for both probability as well as impact are sorted to be dealt with first. For instance, risk such as a tight test schedule can be said to have high probability as well as high impact. Thus, it should be on the top of the priority list. However, a risk such as natural disaster might have a medium to high impact, but its probability is low. Hence, such a risk won’t make it to the top of the Risk Assessment list.
Risk Mitigation/Control
The third step under Risk Management in Testing, pertains to the idea of taking necessary measures and steps for controlling and mitigating the assessed risks. These solutions are not universal and would essentially differ from project to project and even organization to organization. Some of the Risk Management Examples in Software Testing include: one of the risks, as mentioned earlier, was that of a tight test schedule. Since this risk, happens to be a crucial one, it would be important to develop strategies for mitigating the same. This might involve completing the preparatory tasks well in advance and providing for some kind of buffer period from the beginning to make room for any contingency. Another risk identified in the first stage was that of an incomplete definition of scope. In order to mitigate the risk, it will be important to ensure that the project scope is extremely well-defined but, at the same time, is not unrealistically rigid. This is important in order to make room for any kind of imminent change, which, if not incorporated, might harm the project immensely.
Conclusion
It is evident that Risk Management in Testing is not an optional aspect of the Software Development Life Cycle. Risk Management in Software Testing has immense benefits, predominantly in the form of delivering products that can ensure customer satisfaction in the best possible manner.
The Risk Management Process in Software Testing is often meticulously executed to ensure that any unaccounted event does not result in non-accomplishment of the project’s goals and objectives.
The testing team has a crucial role in the overall Risk Management process. In this respect, SDETs who happen to embody the skills of a developer and a tester stand a valuable chance to contribute their meaningful insights.
If you wish to develop skills in consonance with that of an SDET, you can reap the benefits of our QA Automation Testing course. The Syntax Technologies QA Automation Testing course is one of the best in the market, and you would stand a good chance of accomplishing your career objectives in this field. Enrol in our QA Automation course now: