Welcome aboard, aspiring data aficionados!
If you’re relatively new to the data analytics arena, fear not. This isn’t an exclusive club with secret handshakes and complex codes.
Instead, consider it an open invitation to a treasure hunt where the treasure is knowledge, and your map is Data Governance.
Whether you’re just dipping your toes into the data lake or gearing up for a deep dive, learning data governance through a data analytics course can be your compass in this exhilarating journey!
So why is data governance so crucial?
Let’s explore the pivotal role of Data Governance in your aspiring data analytics adventure in this article!
What is Data Governance?
Imagine your data is like a garden, and data governance is the diligent gardener making sure everything grows splendidly.
It’s about taking good care of your data, ensuring it’s accurate and safe, and everyone knows where to find the ripest tomatoes (or, you know, the most valuable insights)!
So, in simpler terms, data governance is like having a green thumb for your information garden, ensuring everything blooms beautifully and stays in tip-top shape.
Now, look at its key features and some examples tethered to them to grasp things more easily!
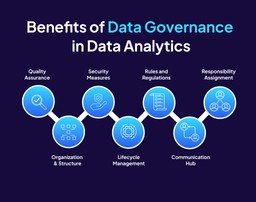
Benefits of Data Governance in Data Analytics
Quality Assurance:
- Ensures your data is accurate and trustworthy.
Example: Implementing validation checks to ensure that customer information in a database is accurate and up-to-date.
Organization and Structure:
- Organizes data for easy access and understanding.
Example: Creating a well-structured folder system for files and documents, making it easy to locate specific information when needed.
Security Measures:
- Protects your data from unauthorized access or misuse.
Example: Setting up user access controls to restrict sensitive financial data only to authorized personnel within an organization.
Lifecycle Management:
- It manages data throughout its entire existence, from creation to retirement.
Example: Establishing protocols for archiving and deleting outdated records or files to maintain a lean and relevant data set.
Rules and Regulations:
- Establishes guidelines for handling and using data.
Example: Developing and enforcing policies regarding data privacy to comply with legal requirements such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Communication Hub:
- Facilitates clear communication about changes and updates in the data.
Example: Implementing a centralized platform or tool for team members to communicate changes, updates, or issues related to the data.
Responsibility Assignment:
- Assigns roles to different data components, ensuring clarity and accountability.
Example: Clearly defining roles such as data stewards responsible for the organization’s accuracy and quality of specific datasets.
Who Takes the Lead in Data Governance?
In the exciting world of data, a fantastic team of individuals ensures everything runs smoothly. Think of them as the data universe superheroes, each with unique powers.
Let’s meet the cast:
Data Stewards:
- Role: These are the everyday heroes, taking care of specific sets of data. They ensure everything is accurate, in order, and ready for action.
Data Owners:
- Role: The ultimate guardians of data realms. They oversee specific data territories, making sure they’re well-protected and serving their purpose.
Chief Data Officer (CDO):
- Role: Meet the big boss! The Chief Data Officer is like the head honcho, guiding the organization’s data strategy and making sure everything aligns with the big picture.
Data Governance Committee/Team:
- Role: Imagine them as the Avengers of the data world. They gather, strategize, and enforce the rules to ensure everyone is on the same page.
IT and Security Professionals:
- Role: These are the tech wizards. They implement the behind-the-scenes magic, setting up security measures and ensuring everything is technically sound.
Data Users (Analysts, Scientists, etc.):
- Role: Everyday champions of data! Analysts use the information responsibly, providing valuable insights and contributing to the overall data journey.
Legal and Compliance Officers:
- Role: The rule keepers. They ensure that everything happening in the data realm follows the law, especially when it comes to privacy and security.
Executive Leadership:
- Role: The cheerleaders and supporters. They provide the resources and encouragement needed to keep the data governance ship sailing smoothly.
Business Units and Department Heads:
- Role: These are the team captains, working closely with the data Avengers to ensure that data serves the specific needs of their departments.
End Users:
- Role: The everyday adventurers in the data world. They follow the rules, report any data hiccups, and actively participate in making the data journey a success.
So, there you have it?the friendly faces behind the scenes, ensuring that the data adventure is a collaborative and successful one!
Effective Data Governance requires a shared commitment from individuals across various organizational roles.
Collaboration, communication, and a clear understanding of respective responsibilities are key to successfully implementing and sustaining robust Data Governance practices.
9 Examples of Data Governance Being Used in Real Life
Here are nine real-life examples of organizations effectively utilizing Data Governance:
JPMorgan Chase & Co.:
- Use Case: JPMorgan Chase employs Data Governance to ensure the accuracy and security of financial data. This includes stringent controls on customer information, transactional data, and compliance with financial regulations.
The Walt Disney Company:
- Use Case: Disney uses Data Governance to manage and protect intellectual property across its vast media empire. This involves ensuring the consistency and accuracy of data related to characters, storylines, and franchise details.
Walmart:
- Use Case: Walmart leverages Data Governance to optimize its supply chain. This includes ensuring the quality of product data, managing inventory information, and streamlining data flow for efficient operations.
Healthcare Systems (e.g., Mayo Clinic):
- Use Case: Healthcare organizations implement Data Governance to maintain patient confidentiality, secure health records, and ensure accurate medical information. Mayo Clinic, for instance, employs Data Governance to uphold the highest standards in patient data management.
Netflix:
- Use Case: Netflix utilizes Data Governance to enhance its recommendation algorithms. By governing user data effectively, Netflix provides personalized content recommendations based on viewing history, preferences, and user behavior.
European Central Bank (ECB):
- Use Case: ECB employs Data Governance to oversee and manage financial data for monetary policy decisions. This involves ensuring the accuracy and consistency of economic indicators and financial market data.
IBM:
- Use Case: As a technology and consulting company, IBM utilizes Data Governance to manage and govern data across its diverse services. This includes ensuring the quality and security of client data and adherence to data privacy regulations.
Telecom Industry (e.g., AT&T):
- Use Case: Telecommunication companies like AT&T implement Data Governance to manage vast amounts of customer data. This includes ensuring the security of customer information, managing call records, and complying with telecommunications regulations.
NASA:
- Use Case: NASA uses Data Governance in managing vast amounts of scientific and engineering data. This involves ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data related to space missions, research, and exploration.
These examples highlight the diverse applications of Data Governance across industries, emphasizing its role in ensuring data quality, security, and compliance with regulations in real-world scenarios.
What are the Tools for Data Governance?
Several data tools are available to facilitate and enhance Data Governance initiatives within organizations.
These tools are designed to manage, monitor, and enforce data policies, ensuring data integrity, security, and compliance across its lifecycle.
Here are some commonly used tools for Data Governance:
- Collibra:
The Data Librarian: Collibra takes on the role of a meticulous data librarian, ensuring every piece of data is cataloged, organized, and ready for exploration.
- Informatica Axon:
Translator of Tech Talk: Informatica Axon is a skilled translator, turning complex data terminology into a language that tech-savvy data experts and business enthusiasts can understand. It’s the bridge between the data realm and the business world.
- IBM InfoSphere Information Governance Catalog:
Data Steward Extraordinaire: Think of IBM’s tool as the reliable data steward, overseeing and curating the information landscape. It’s the guardian ensuring data quality and adherence to governance principles.
- Alation:
Data Pathfinder: Alation is a data trailblazer, guiding you through the expansive data landscape with cataloging and collaboration tools. It’s your GPS for navigating the data wilderness.
- Erwin Data Intelligence Suite:
Swiss Army Knife of Data Governance: Erwin’s suite is like a versatile tool, offering a range of functions from metadata management to data lineage. It’s your all-in-one companion for navigating the complexities of data governance.
- SAS Data Governance:
Wizard Behind the Data Curtain: SAS Data Governance is the magical enchanter of the data world. It weaves spells of business glossaries, data lineage, and policy management, bringing a touch of magic to data governance.
- Azure Purview (formerly Azure Data Catalog):
Cloud Navigator: Azure Purview acts as a navigator in the cloud, helping you chart your course through data cataloging, classification, and governance.
- Collaborative Data Governance (CDG) by Global IDs:
Data Governance Maestro: CDG by Global IDs orchestrates a symphony of data governance, ensuring metadata, data quality, and cataloging harmonize seamlessly.
- Talend Data Catalog:
Data Explorer’s Toolkit: Talend Data Catalog equips you with the tools of a data explorer. It’s your toolkit for cataloging, metadata management, and data quality?a compass for the modern data adventurer.
- Ataccama ONE:
Unified Data Command Center: Ataccama ONE is your command center for unified data governance. It takes charge, ensuring data cataloging, metadata management, and data quality work together cohesively. It’s the captain of your data ship.
The Data Governance process can vary significantly based on several factors, including the size and complexity of the organization, the scope of the Data Governance initiative, and the level of maturity of existing data management practices.
Here are some considerations regarding the duration of the Data Governance process:
Is the Data Governance Process Time-Consuming?
Initial Setup
Setting up the initial framework, policies, and governance structure can take some time, especially if the organization is starting from scratch.
The complexity of defining roles, responsibilities, and governance policies, as well as the level of organizational alignment, can impact the duration of the setup.
Cultural Shift
Achieving a cultural shift towards a data-driven mindset and fostering a commitment to Data Governance principles may take time.
Existing organizational culture, employee awareness, and the effectiveness of change management efforts can influence the speed of this shift.
Data Quality Improvement
Improving data quality, a key aspect of Data Governance, is an ongoing process that may take time to yield measurable results.
The extent of data quality issues, the complexity of data sources, and the efficiency of data quality improvement processes can impact the duration.
Compliance and Security Implementation
Implementing security measures and ensuring compliance with regulations can be an ongoing effort.
The complexity of regulatory requirements, the need for technology implementations, and the thoroughness of security measures can affect the timeline.
Training and Communication
Training employees, fostering data literacy, and effective communication are ongoing efforts that require consistent reinforcement.
The size of the organization, the complexity of data concepts, and the frequency of communication efforts influence the time needed for these activities.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Continuous monitoring of Data Governance metrics and the iterative improvement of processes are ongoing activities.
The efficiency of monitoring tools, the responsiveness to issues, and the organization’s commitment to continuous improvement influence the duration.
While implementing Data Governance does require an investment of resources, the benefits?such as improved data quality, enhanced decision-making, and better compliance?can outweigh the efforts.
It’s essential for organizations to view Data Governance as a strategic, long-term investment in the quality and reliability of their data assets.
How to Get Started with Data Governance as a Newbie
Embarking on the journey of Data Governance as a newbie might seem like stepping into a new galaxy, but fear not?here’s a beginner-friendly guide to get you started on this exciting adventure:
Understand the Basics:
Begin by grasping the fundamental concepts of Data Governance. Familiarize yourself with metadata, data quality, data assets, and data stewardship.
Online resources, introductory courses, and beginner-friendly books are excellent starting points.
Define Your Goals:
Clarify your objectives. What do you want to achieve with Data Governance? Whether it’s ensuring data accuracy, improving data security, or complying with regulations, having clear goals will guide your learning journey.
Learn from Experts:
Dive into the vast ocean of knowledge by learning from experienced practitioners. Attend webinars, workshops, and conferences, and listen to podcasts on Data Governance.
Platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter are excellent for connecting with experts in the field.
Explore Data Governance Frameworks:
Familiarize yourself with popular Data Governance frameworks such as DAMA-DMBOK (Data Management Body of Knowledge) or COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies).
These frameworks provide structured approaches to implementing Data Governance.
Start Small:
Don’t feel overwhelmed. Begin with a small, manageable project. Choose a specific dataset or data process to apply Data Governance principles. This hands-on experience will build your confidence.
Identify Stakeholders:
Recognize the critical players in your organization who are involved in or impacted by data processes. Establishing good relationships early on is crucial for successful Data Governance.
Create a Data Dictionary:
Start building a simple data dictionary. Document the definitions and meanings of key data elements. This will serve as a reference for everyone involved in data-related activities.
Attend Training Programs:
Enroll in beginner-friendly courses or certifications on Data Governance. Many online platforms offer courses tailored for beginners, providing a structured learning path.
Network with Peers:
Join online forums, communities, or social media groups related to Data Governance. Engaging with peers allows you to share experiences, ask questions, and learn from others in the field.
Stay Curious and Adaptive:
The data landscape evolves, so embrace a mindset of continuous learning. Stay curious about emerging trends and technologies in Data Governance, and be adaptive to changes in the field.
Remember, every journey starts with a single step. As a newcomer to Data Governance, take your time to explore, learn, and apply the concepts gradually.
Soon enough, you’ll find yourself navigating the data galaxy with confidence!
Empowering Your Data Journey with Syntax Technologies
The real-world applications of Data Governance showcased here reveal its transformative power across diverse industries.
Understanding the frameworks that shape data becomes pivotal as we delve into the data landscape.
With its expertise, Syntax Technologies is a guiding light in deciphering the complexities of data governance frameworks like SQL.
Navigating through these frameworks is akin to unlocking the secrets of data orchestration.
Whether you’re a seasoned data professional or a newcomer exploring the vast landscapes of data governance, Syntax Technologies provides the tools and knowledge to comprehend and leverage the frameworks underpinning data’s reliability, security, and strategic use.
As you embark on this journey, remember: in the realm of data, knowledge is not just power; it’s the key to unlocking a world of endless possibilities.